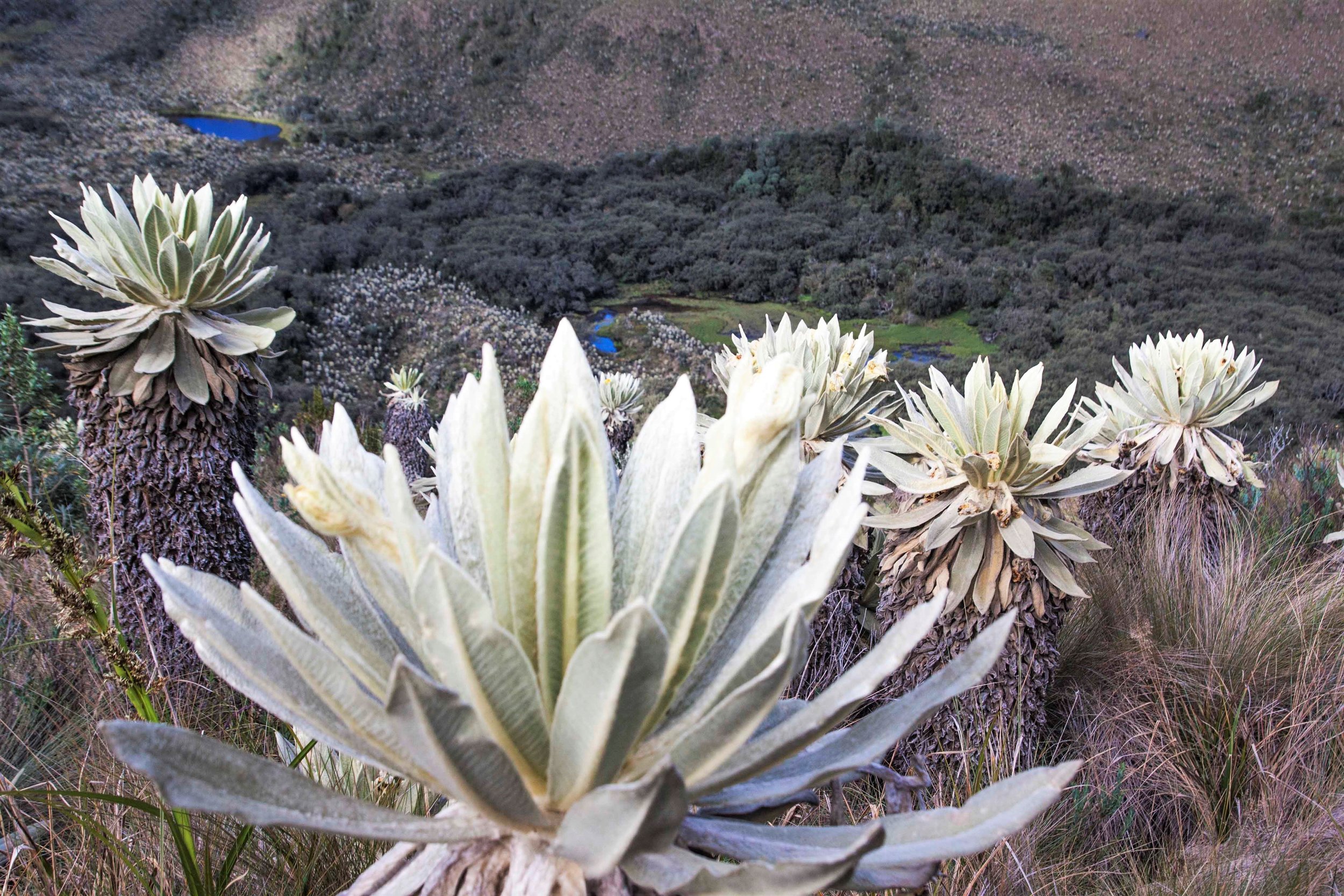
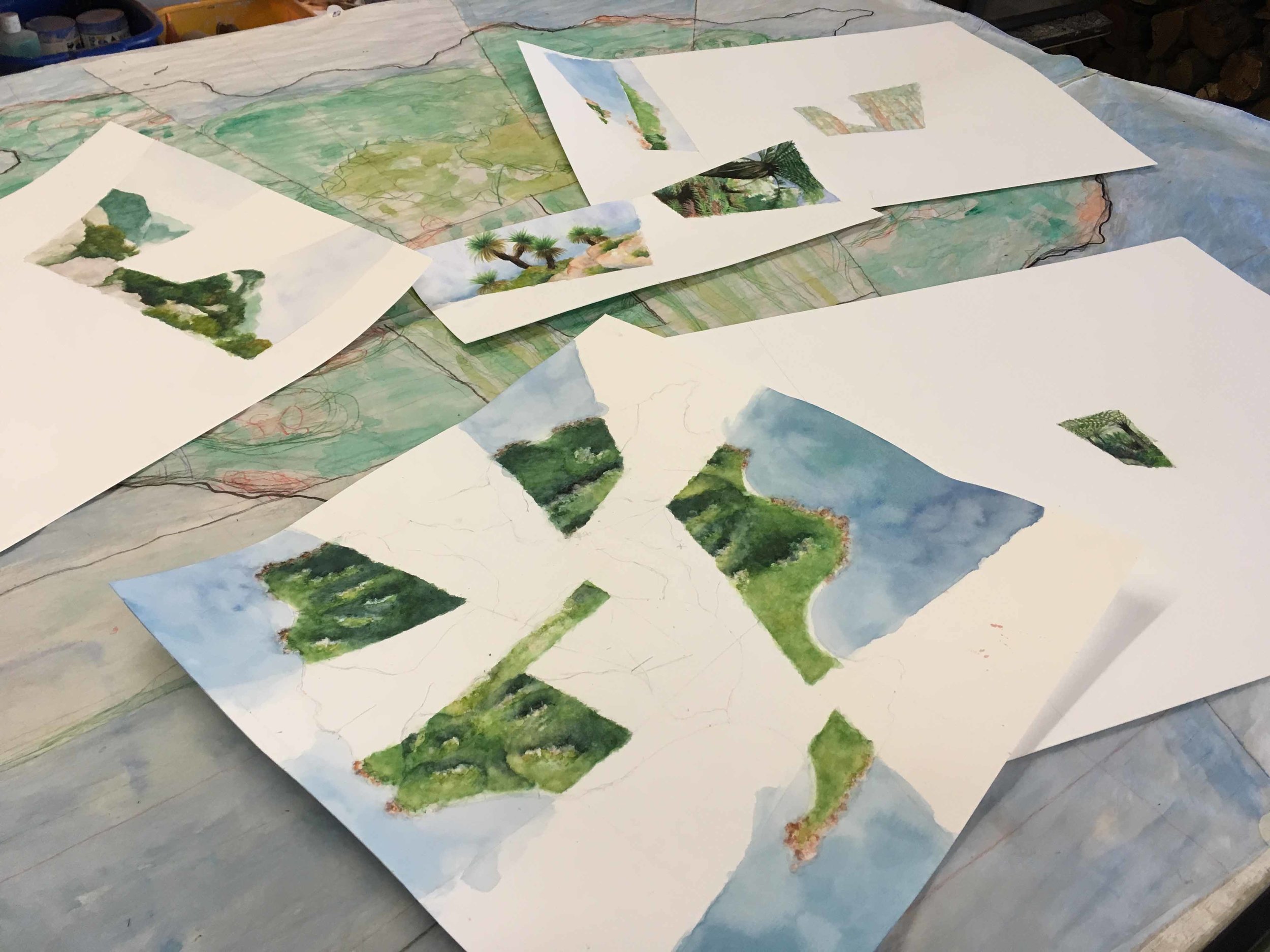
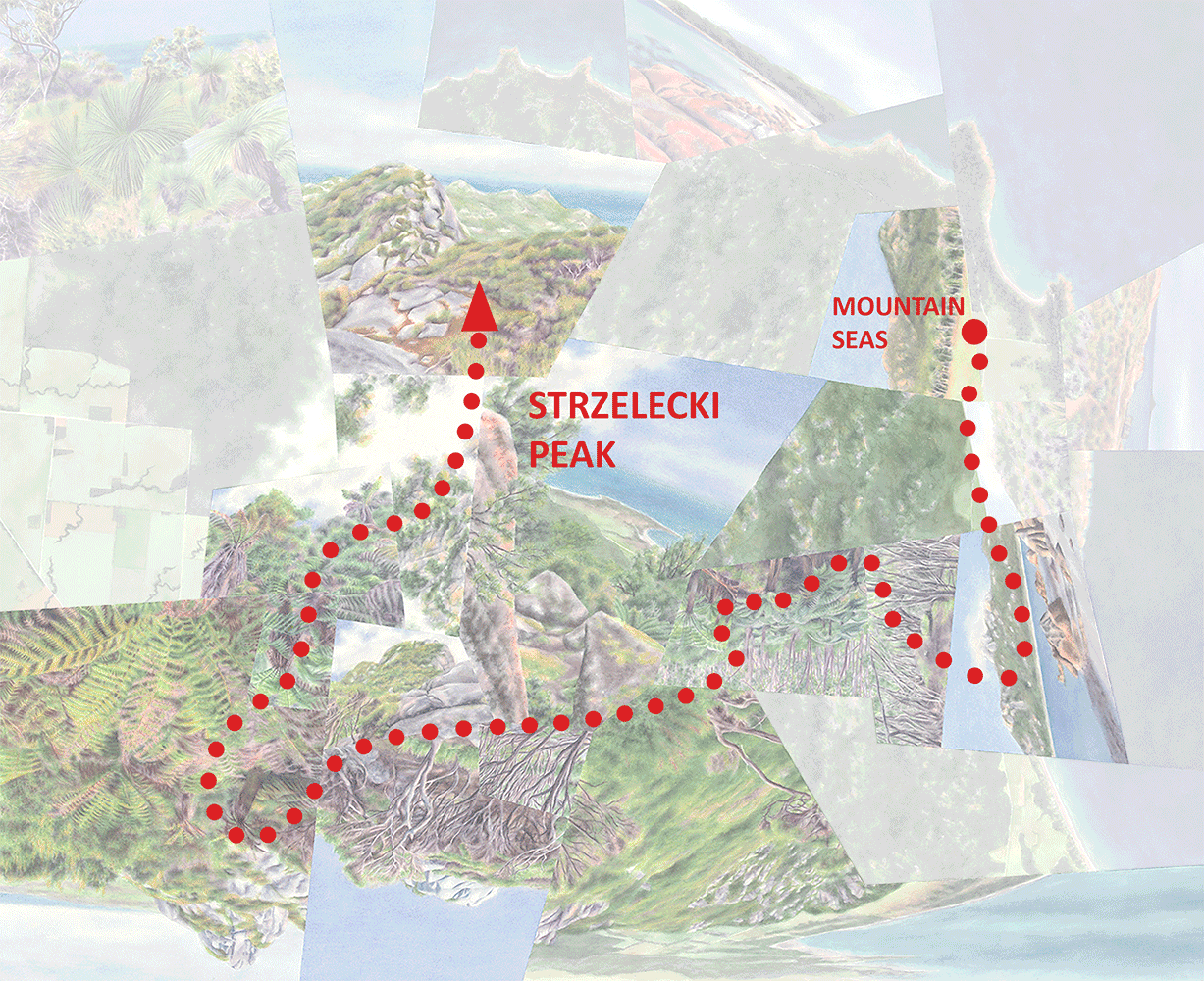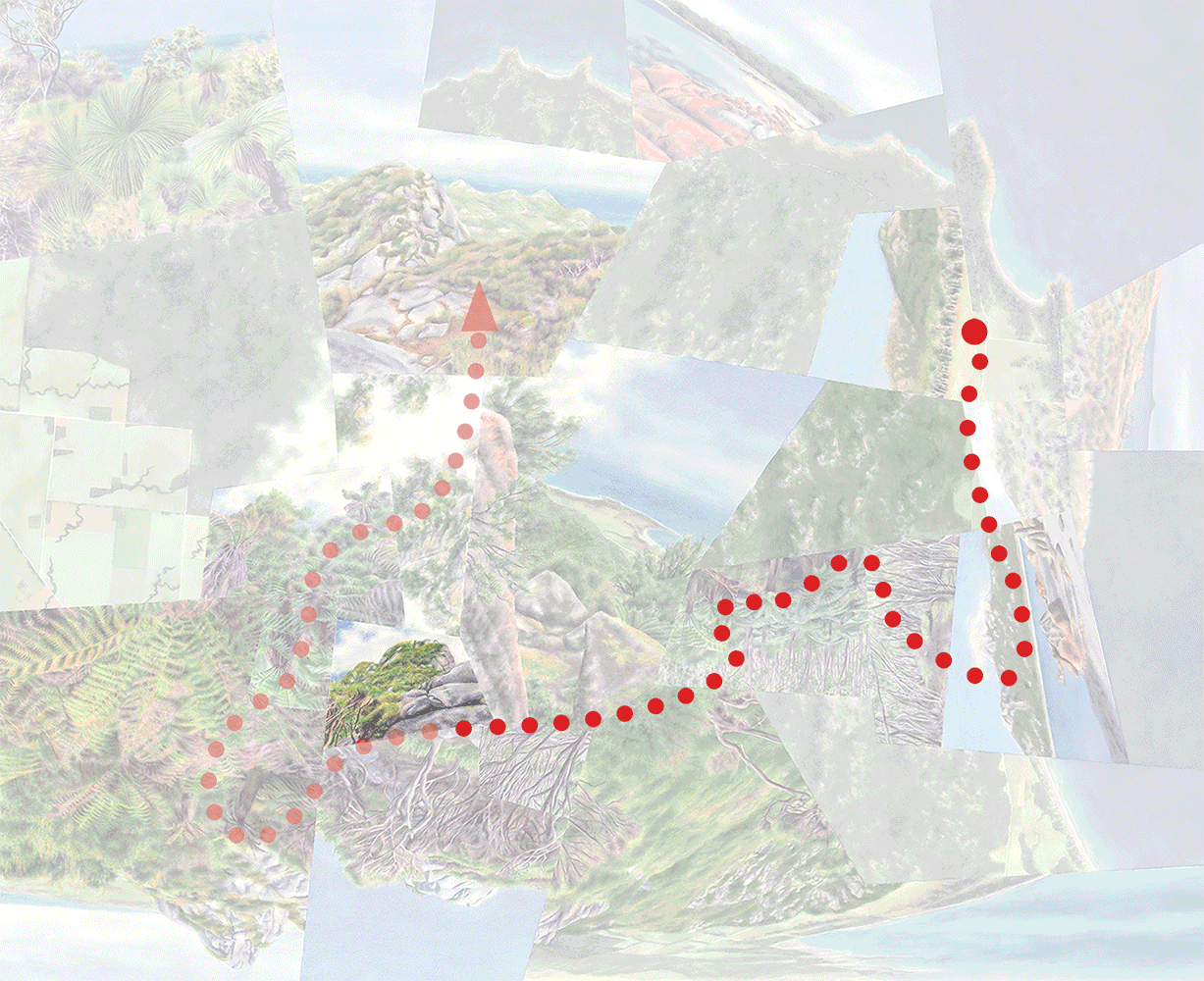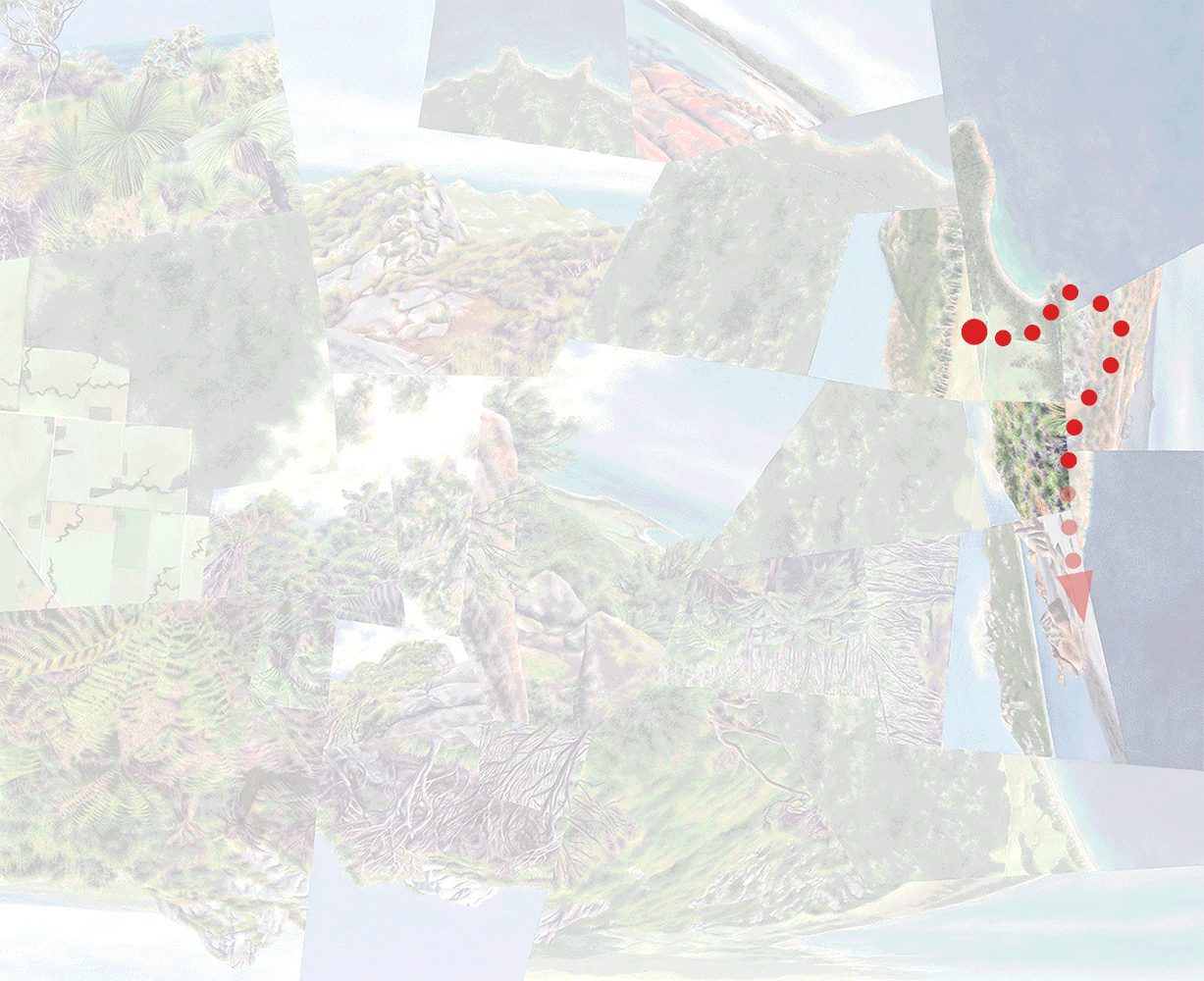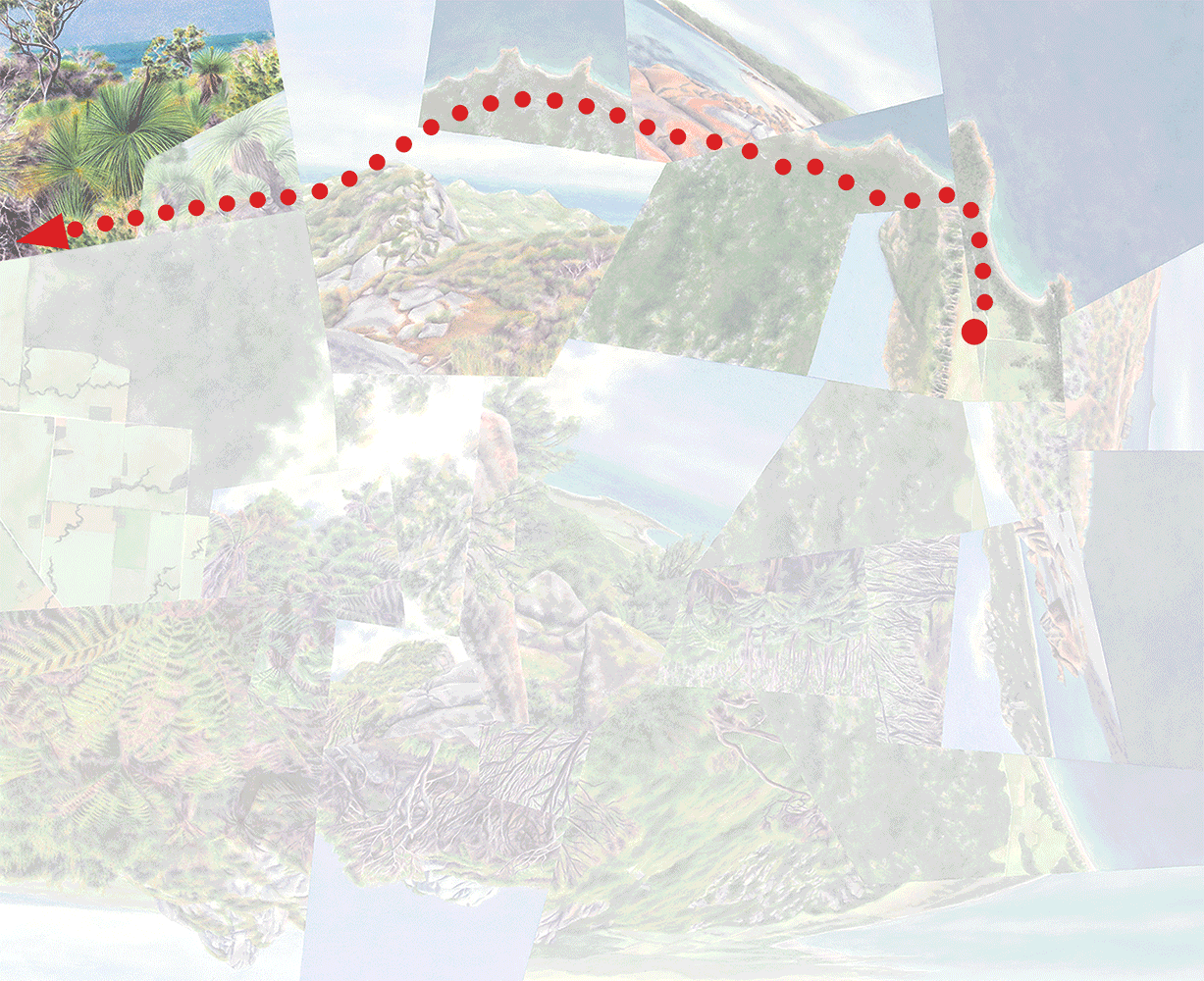
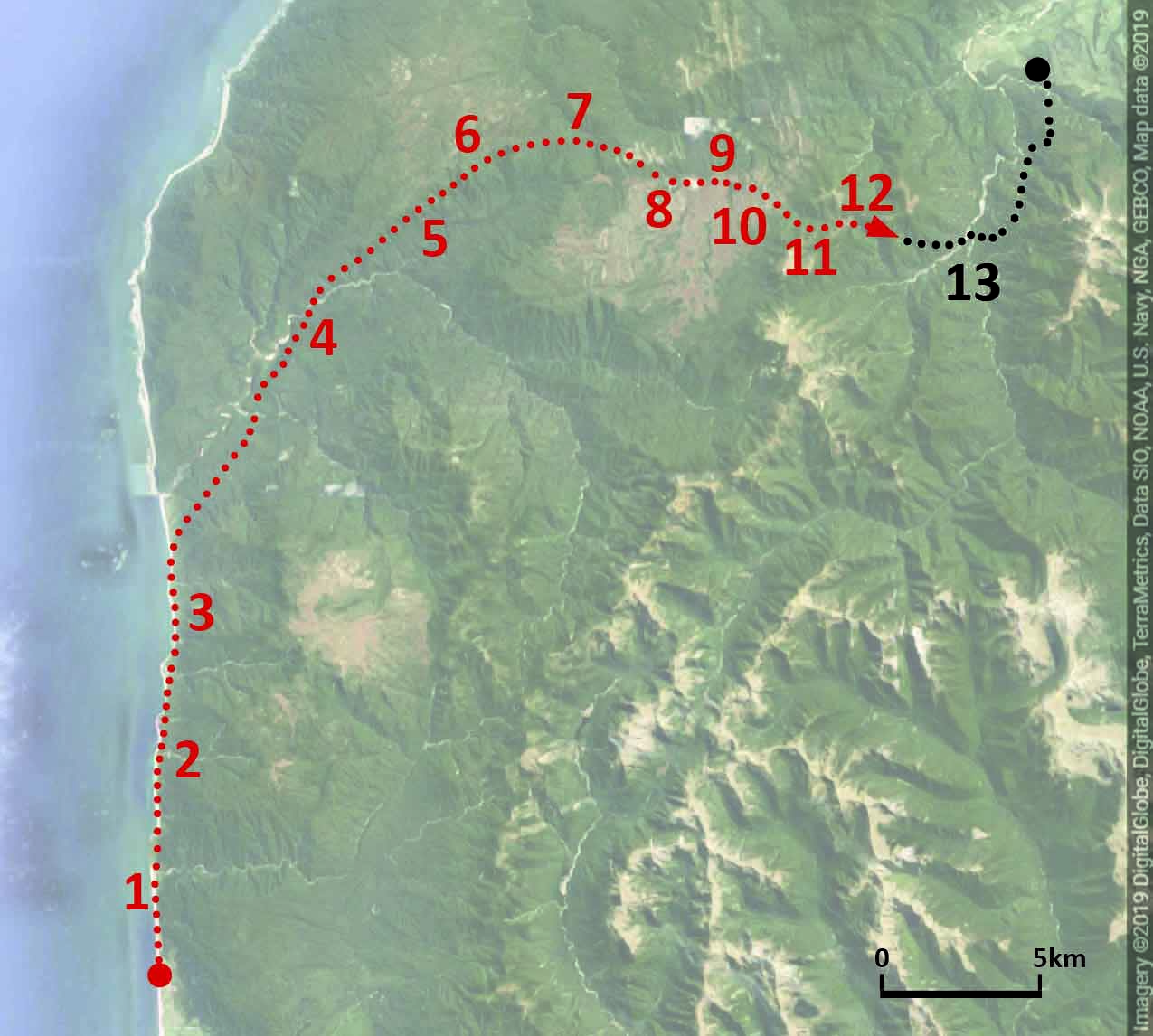
La Gomera, with points of interest along the north-south journey depicted in Divide. The dashed line roughly traces the wet-dry divide itself.
My last post focused on my impressions of Tenerife, the largest and tallest of the Canary Islands. Here I’ll move on to La Gomera—smaller, lower, and older with much more eroded topography overall. (You might compare Tenerife and La Gomera to the Big Island of Hawaii and Kauai, respectively.) Reaching only about 5000’ La Gomera lacks pine and alpine zones, but its contrasts between wet and dry are in fact even more dramatic than on Tenerife. The upper elevations of the northern half of La Gomera are mostly contained within Garajonay National Park, protecting the world’s largest remaining tract of laurisilva (a unique form of temperate cloud forest), while its southern half, particularly at lower elevations, is mostly semi-desert if not true desert.
So, while the lowlands are generally drier than the uplands throughout, there’s a clear and dramatic division between the northern and southern halves of the island. Hence the title of Divide, which depicts a sequence of experiences traveling across the island from north to south. (Unlike Great Walk, which represents a linear journey along a single defined route in New Zealand, Divide is more haphazard in that it combines travel along several different drives and hikes.)
Divide, watercolor on paper, 20”x20”.
The journey begins in the town of Hermigua (#1 on the annotated version) in an agricultural valley near the north coast with a more-or-less Mediterranean climate. Hiking up into the valley the climate gets wetter and the fields give way to laurisilva, at first scrubby with scattered date palms (#2) and then growing taller and more lush approaching the National Park. In the Park itself (#3-5), it towers in the river valleys but takes on a more windswept character along the ridges.
At the southern edge of the park comes the “divide” itself. Sadly the island’s highest point, Alto de Garajonay (#6), wasn’t also a figurative high point of the experience. In 2012 a fire ravaged the southwest corner of the National Park including the peak itself, leaving only bare trunks, and at the time I was there clouds obscured views of the arid southern half of the island. (I based the painted view on an image from one of the interpretive displays, rather than one of my own photos.) Yet the low stature of the trunks, plus a few small patches of scrubby but intact vegetation, did reveal a change from the much more luxuriant forest just a few meters to the north.
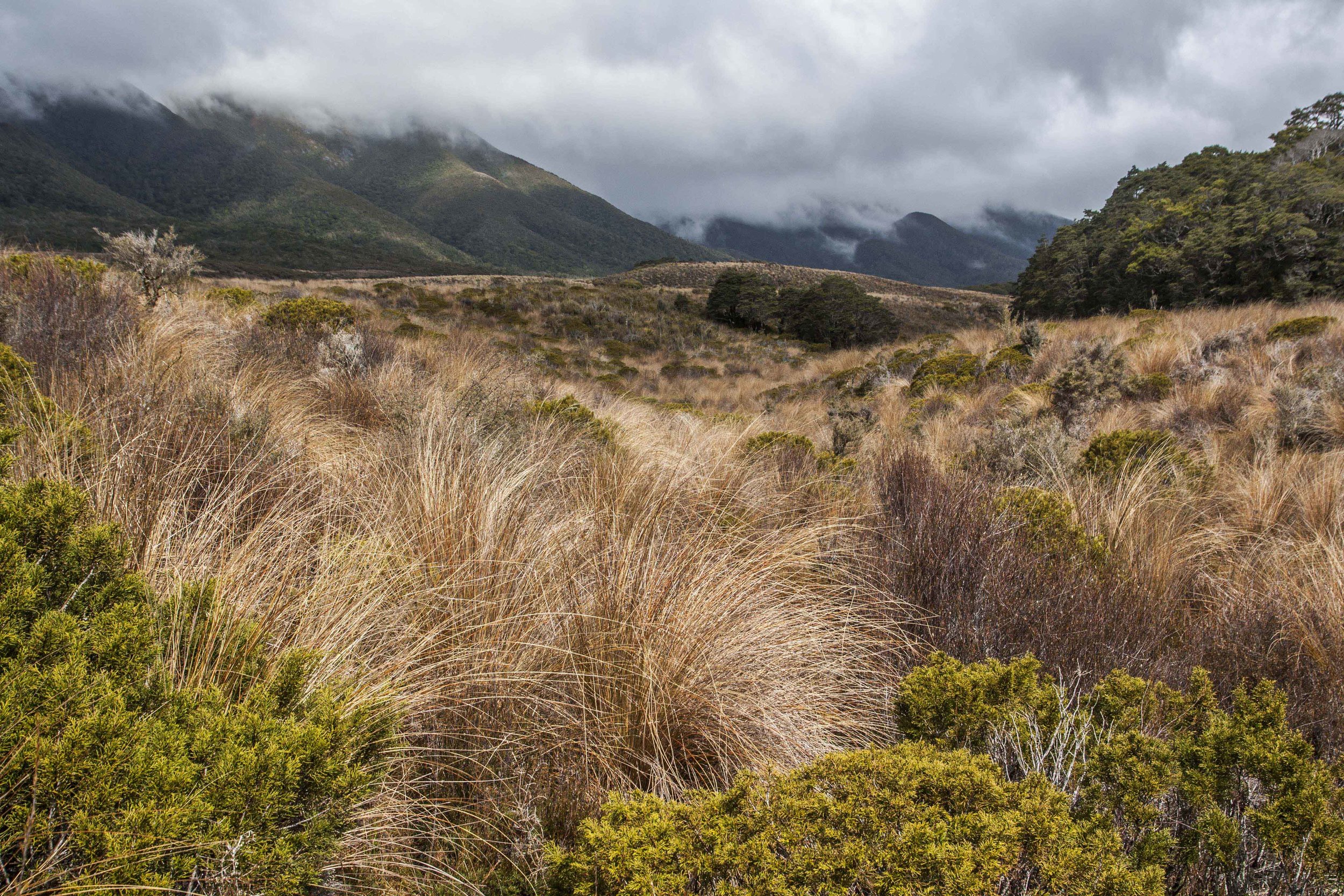
After driving east to escape the fire damage, I dropped below the divide and out from under the clouds, and found another intact patch of what looked like low transitional forest (#7) between the rainforest and semi-desert. It seemed to weirdly evade description—scrubby but not “dry” like a dry forest, yet also not “wet” like the stunted forest found along ridgetops in the National Park. It had been difficult for me to visualize what that transitional zone would look like, and it turned out to be similarly difficult even when I was there. Given the uniqueness of the locale, I think that’s exactly how it should’ve been.
From a point just south of that transitional forest was a view of the Roque de Agando (#8), a famous granite peak surrounded by bits of similar scrubby vegetation, and a glimpse of the drier valley beyond. From there I drove through a progressively more barren landscape to the town of Playa Santiago on the southern coast, from where a short hike led to views of desert gorges and coastline (#9).
Lower reaches of the laurisilva with scattered Phoenix canariensis.
Laurisilva in a stream valley, Garajonay National Park.
Scrubby transitional forest in the vicinity of Alto de Garajonay.
Transitional forest just below the divide.
Desert coastline near Playa Santiago.
The experience of the “divide” itself (the transitional forest) made the strongest impression on me, mostly because the wet-dry transition is so rapid as to make the transitional forest clearly an edge rather than a recognizable ecosystem in itself, creating that empowering feeling of straddling two environments typically many miles apart. It felt as if fire and other impacts had spared those few tiny patches just for me. Still, those patches are isolated, no longer connected to intact habitat on either side. Needless to say I was frustrated that I hadn’t somehow “known” to visit the island before the 2012 fire when such connections, with trail access, did exist in the vicinity of Alto de Garajonay. It underscores the delicacy of these island environments, and it’s thankful that the fire didn’t spread further into the National Park.
Forest burnt in the 2012 fire, with Alto de Garajonay in the background.
And now I disappear to Chile for a month and a half (assuming the country doesn’t spin any more out of control before I leave in a week)—but first, for those of you in the Bay Area, a final reminder for my Open Studio this coming weekend! (Information below, and note that because it’s my birthday the day after, not to mention Halloween, I may up the ante on the goodies….come help me celebrate!)
Darren